OneScript® Plus cDNA Synthesis Kit
| Cat# | Unit |
|---|---|
| G236 | 100 rxn |
Documents
Description
Description
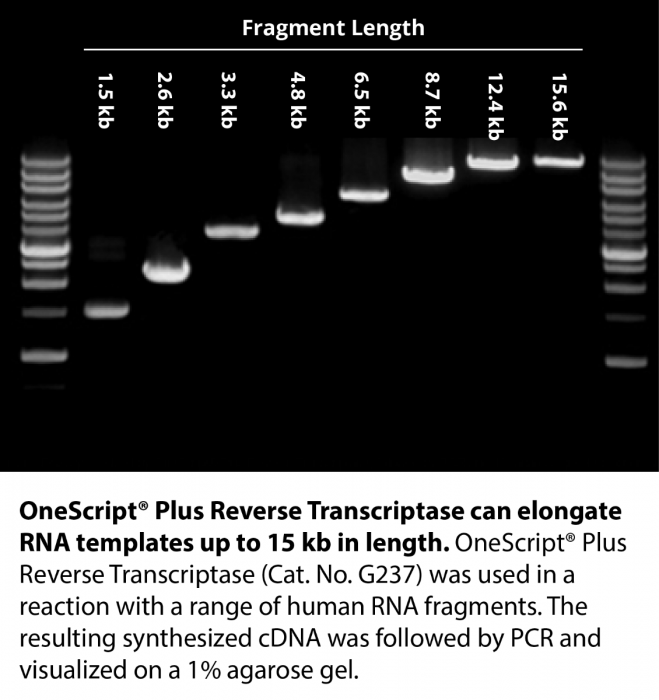
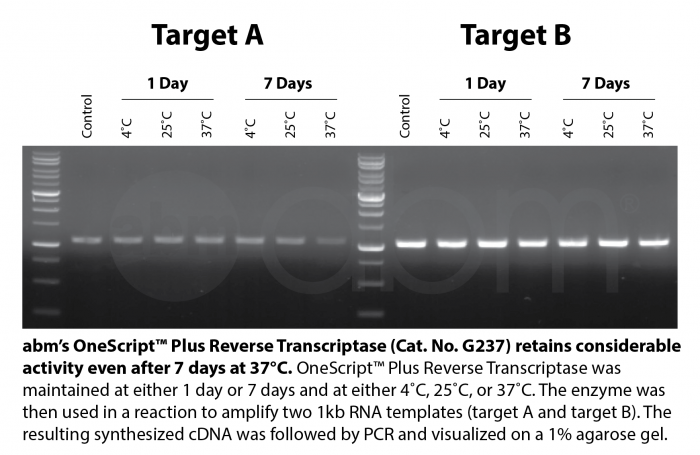
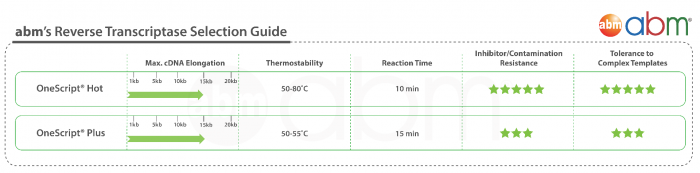
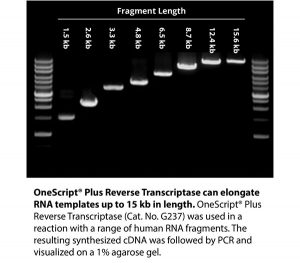
OneScript® Plus cDNA Synthesis Kit contains a Moloney-Murine Leukemia Virus Reverse Transcriptase with genetic modifications to abolish RNase H activity to achieve thermal stability. This special mutant enzyme offers higher cDNA yields, longer cDNA up to 12 kb, and is able to perform under high temperatures (50°C – 55°C), facilitating the elimination of secondary structures associated with GC-rich RNA templates. OneScript® Plus is formulated with abm’s RNaseOFF Ribonuclease Inhibitor offering improved resistance to oxidation compared to the high oxidation-sensitive human RNase inhibitors. RNaseOFF is stable even under very low concentrations of DTT (< 1 mM), making it the best choice for ultimate RNA protection.
Key Features
- Maximal flexibility in priming – oligo(dT), random primers or gene-specific primers
- Robust cDNA synthesis from any RNA template
- High reproducibility and excellent yield
- Employs abm‘s OneScript® Plus Reverse Transcriptase (Cat. No. G237)
- Earn 2X the rewards points
| PRODUCT COMPONENT | QUANTITY |
|---|---|
| OneScript® Plus Reverse Transcriptase | 100 rxn (100 µl) |
| 5X RT Buffer | 400 µl |
| Oligo(dT) (10 μM) | 100 µl |
| Random Primers (10 μM) | 100 µl |
| dNTP (10 mM) | 100 µl |
| Nuclease-Free H2O | 2 x 1.0 ml |
| SKU | G236 |
|---|---|
| Applications |
|
| Storage Condition | Store at -20°C. |
| Unit Quantity | 100 rxn |
Supporting Protocol
MSDS
QC
Other
- Menon, V et al. “The contribution of visceral fat to improved insulin signaling in Ames dwarf mice” Aging Cell 13 (3):497-506 (2014). DOI: 10.1111/acel.12201. PubMed: 24690289. Application: Reverse Transcription.
- Lee, G et al. “Potential monoclonal antibody therapy for the treatment of ovarian cancer” Ovarian cancer—basic science perspective :385-406 (2012). DOI: 10.5772/1268 . Application: Reverse Transcription.
- Menon, V et al. “The contribution of visceral fat to improved insulin signaling in Ames dwarf mice” Aging Cell. 13(3):497-506 (2014). DOI: 10.1111/acel.12201. PubMed: 24690289. Application: Reverse Transcription.
- Juskeviciute, E et al. “Inhibition of miR-21 rescues liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in ethanol-fed rats” Amer. J. Physiol.-Gastrointestinal and Livery Physiology 5:G794-G806 (0). DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00292.2016 .
- Amodio, G et al. “Identification of a microRNA (miR-663a) induced by ER stress and its target gene PLOD3 by a combined microRNome and proteome approach” Cell Bio. Toxicol. 285: (2016). DOI: 10.1007/s10565-016-9335-z.
- Antony, A et al. “MICU1 regulation of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake dictates survival and tissue regeneration” Nat. Comm. : (2016). DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10955.
- Lakshmi , K et al. “A novel comparative pattern analysis approach identifies chronic alcohol mediated dysregulation of transcriptomic dynamics during liver regeneration” BMC Genomics 1:1 (2016). DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-2492-x.
- Maher, SK et al. “Rethinking the biological relationships of the thyroid hormones, l-thyroxine and 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine” Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D: Genomics Proteomics :44-53 (2016). DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cbd.2016.04.002.
- Diana, D et al. “Inhibition of autocrine signaling of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in breast cancer” : (2016).
- Park, H-S et al. “PPARγ neddylation essential for adipogenesis is a potential target for treating obesity” Cell Death Diff. :45-57 (2016). DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.018.
- Gao, J., Song, J., Du, M., & Mao, X. “Bovine α-lactalbumin hydrolysates (α-LAH) attenuate high-fat diet induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating hepatic lipid metabolism in C57BL/6J mice” Journal of Functional Foods 54:254–262 (2019). DOI: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.01.027.
- Saliba, J., Coutaud, B., Solovieva, V., Lu, F., & Blank, V. “Regulation of CXCL 1 chemokine and CSF 3 cytokine levels in myometrial cells by the MAFF transcription factor” Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 23(4):2517–2525 (2019). DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14136.
- ŞEN, A., Ayar, B., Yilmaz, A., ACAR, Ö. Ö., Turgut, G. C., & TOPÇU, G. “Natural diterpenoid alysine A isolated from Teucrium alyssifolium exerts antidiabetic effect via enhanced glucose uptake and suppressed glucose absorption” Turkish Journal of Chemistry 43(5):1350-1364 (2019).
- Sun, L., Pang, Y., Wang, X., Wu, Q., Liu, H., Liu, B., … Jiang, C. “Ablation of gut microbiota alleviates obesity-induced hepatic steatosis and glucose intolerance by modulating bile acid metabolism in hamsters” Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 9(4):702–710 (2019). DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.02.004.
- Wu, F., Niu, Z., Zhou, B., Li, P., & Qian, F. “PSMB1 Negatively Regulates the Innate Antiviral Immunity by Facilitating Degradation of IKK-ε” Viruses 11(2):99 (2019). DOI: 10.3390/v11020099.
- Zhao, G., Zhang, T., Sun, H. J., & Liu, J. “Copper nanoparticles induce zebrafish intestinal defects via endoplasmic reticulum and oxidative stress” Metallomics. : (2019).