BlasTaq™ 2X PCR MasterMix
| Cat# | Unit |
|---|---|
| G895 | 800 rxn (10.0 ml) |
Documents
Description
Description
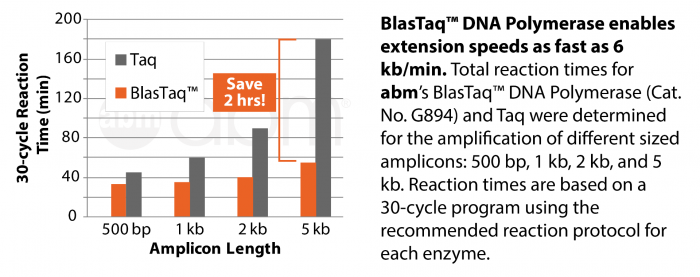
Blast through a routine 2 hour PCR run in only 20 minutes!
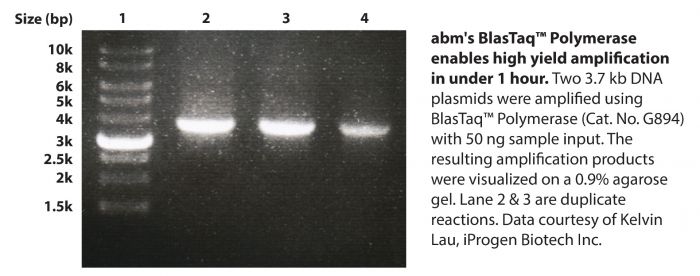
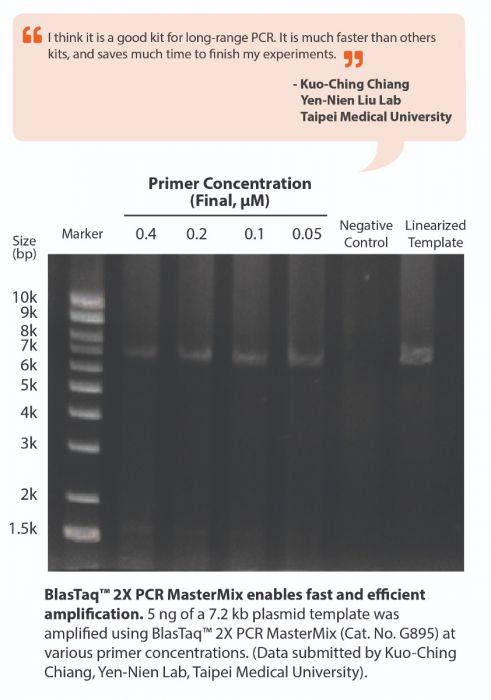
BlasTaq™ 2X PCR MasterMix is a ready-to-use MasterMix containing abm’s BlasTaq™ DNA Polymerase in a uniquely-formulated buffer with gel loading dye. BlasTaq™ DNA Polymerase is a strategically-engineered, next generation Taq Polymerase that has rapid extension rates and robust performance. With specialized reaction conditions, this polymerase provides increased processivity, yields, and sensitivity, while shortening reaction times by up to 70%, compared to wild-type Taq DNA polymerase. BlasTaq™ has 5’-3’ polymerase and 5’-3’ exonuclease activities, lacks 3’-5’ exonuclease activity, and produces 3’-dA-tailed amplicons. PCR products made with BlasTaq™ can be used with TA cloning vectors.
Product Features:
- 6 kb/min extension speed
- 40-70% less time needed than reguar Taq
- Superior senstivitiy
- Earn 2X the rewards points
| SKU | G895 |
|---|---|
| Applications |
|
| Concentration | 2X |
| Storage Condition | Store at -20°C. This product is stable for 2 years from the date of shipping if stored and handled properly. |
| Unit Quantity | 800 rxn (10.0 ml) |
Supporting Protocol
MSDS
QC
Other
- Chung, G et al. “CHL-1 provides an essential function affecting cell proliferation and chromosome stability in Caenorhabditis elegans” DNA Repair (Amst.) 10 (11):1174-1182 (2011). DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.09.011. PubMed: 21968058. Application: PCR.
- Yang, S., Tian, M., & Johnson, A. N. (2020). SARS-CoV-2 protein ORF3a is pathogenic inDrosophilaand causes phenotypes associated with COVID-19 post-viral syndrome. SARS-CoV-2 Protein ORF3a Is Pathogenic in Drosophila and Causes Phenotypes Associated with COVID-19 Post-Viral Syndrome. Published. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.20.423533
- Costarelli, A., Cannavò, S., Cerri, M., Pellegrino, R. M., Reale, L., Paolocci, F., & Pasqualini, S. (2021). Light and Temperature Shape the Phenylpropanoid Profile of Azolla filiculoides Fronds. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12. doi:10.3389/fpls.2021.727667