Taq DNA Polymerase
| Cat# | Unit |
|---|---|
| G009 | 200 rxn |
Documents
Description
Description
Your cost-effective choice for routine amplification!
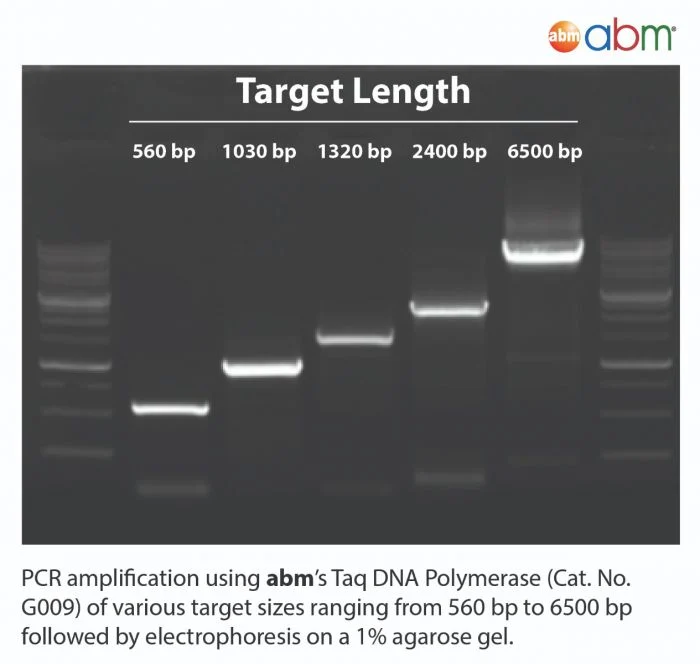
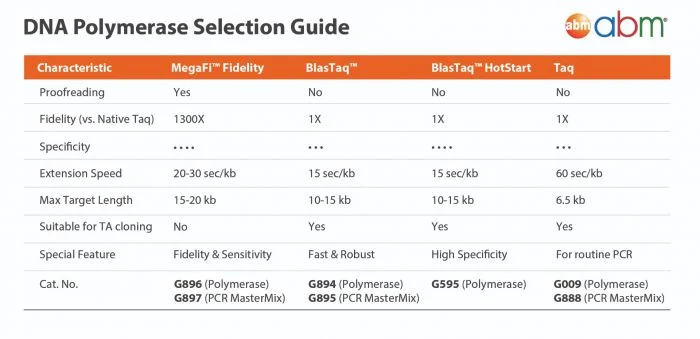
Taq DNA Polymerase is a highly thermostable DNA Polymerase that catalyzes the 5’-3’ synthesis of DNA. This polymerase has 5’-3’ exonuclease activities, lacks 3’-5’ exonuclease activity, and produces 3’-dA-tailed amplicons. PCR products made with Taq can be used with TA cloning vectors.
Product Features:
- Consistent results over a wide range of DNA templates
- Excellent yield and sensitivity
- Ready-to-use mastermix is also available
- Earn 2X the rewards points
| PRODUCT COMPONENT | QUANTITY |
|---|---|
| Taq DNA Polymerase | 200 rxn (200 µl) |
| 5X Taq Buffer 1 | 2 x 1.0 ml |
| SKU | G009 |
|---|---|
| Storage Condition | Store at -20°C. |
| Unit Quantity | 200 rxn |
Supporting Protocol
Other
Does the polymerase leaves a poly-A tail?
It doesn’t leave a poly-A tail but it does leave an “dA” overhang at the 3′ ends.
- Chung, G et al. “CHL-1 provides an essential function affecting cell proliferation and chromosome stability in Caenorhabditis elegans” DNA Repair (Amst.) 10 (11):1174-1182 (2011). DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.09.011. PubMed: 21968058. Application: PCR.
- Nemli, S et al. “Genetic diversity and population structure of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) accessions through retrotransposon-based interprimer binding sites (iPBSs) markers” Turk J Agric For 6:940-948 (2015).
- Yilmaz, O et al. “Genetic relationships among four Turkish sheep breeds using microsatellites” Turkish Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences 39(5):576-582 (2015). DOI: 10.3906/vet-1411-46. Application: PCR.
- Yilmaz, O et al. “Power of different microsatellite panels for paternity analysis in sheep” Animal Sci. Papers and Rep. 2:155-164 (2016).
- Hanson, M et al. “Immune genes and divergent antimicrobial peptides in flies of the subgenus Drosophila” BMC 1:228 (2016). DOI: 10.1186/s12862-016-0805-y.
- Cilvez, P., & Turkyilmaz, S. “Molecular Diagnosis of Candida Species Isolated from Cases of Subclinical Bovine Mastitis” Israel Journal of Veterinary Medicine 73(3):134–140. Retrieved from (2019).
- de Jesus, P. B., Nauer, F., de Mattos Lyra, G., de Araújo, V. L., de Carvalho, I. A. S., de Castro Nunes, J. M., … & Schnadelbach, A. S. . “Phylogenetic relationships within the genus Hypnea (Cystocloniaceae, Rhodophyta): convergent evolution and its implications in the infrageneric classification” Botanica Marina. : ().
- Hamilton, P. T., Hodson, C. N., Curtis, C. I., & Perlman, S. J. “Genetics and Genomics of an Unusual Selfish Sex Ratio Distortion in an Insect” Current Biology 28(23):3864–3870.e4 (2018). DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.10.035.
- KESKİN, Mahmut. “Microsatellite panels for parentage testing of Kilis goats reared in Turkey” Turkish journal of veterinary and animal science 43(1):94-101 (2019). DOI: 10.3906/vet-1809-21.
- Li, J., Liu, X.B., Zhao, Z.W., Yang, Z.L. “Genetic diversity, core collection and breeding history of Pleurotus ostreatus in China” Mycoscience 60(1):14-24 (2019). DOI: 10.1016/j.myc.2018.07.002.
- Liu, Q., Guo, X., Xun, G., Li, Z., Chong, Y., Yang, L., … Feng, Y. “A-Star, an Argonaute-directed System for Rare SNV Enrichment and Detection” : (2019). DOI: 10.1101/803841.
- Paltrinieri, S., Zambon, Y., Mori, N., Canel, A., Bertaccini, A., & Contaldo, N. “Phytoplasmas detected in insects and spontaneous vegetation near vineyards with yellows diseases in Italy” Phytopathogenic Mollicutes 9(1):55 (2019). DOI: 10.5958/2249-4677.2019.00028.8.