Perfecta qPCR Tough Mix
| Products | Kit Size | Order Info |
|---|---|---|
| PerfeCTa qPCR ToughMix | 250 x 20 μL rxns (2 x 1.25 mL) | Order (95112-250) |
| 1250 x 20 μL rxns (10 x 1.25 mL) | Order (95112-012) | |
| 5000 x 20 μL rxns (1 x 50 mL) | Order (95112-05K) | |
| PerfeCTa qPCR ToughMix ROX | 1250 x 20 μL rxns (10 x 1.25 mL) | Order (95113-012) |
| 5000 x 20 μL rxns (1 x 50 mL) | Order (95113-05K) | |
| PerfeCTa qPCR ToughMix Low ROX | 250 x 20 μL rxns (2 x 1.25 mL) | Order (95114-250) |
| 1250 x 20 μL rxns (10 x 1.25 mL) | Order (95114-012) | |
| 5000 x 20 μL rxns (1 x 50 mL) | Order (95114-05K) | |
| PerfeCTa qPCR ToughMix UNG | 1250 x 20 μL rxns (10 x 1.25 mL) | Order (95138-012) |
| 5000 x 20 μL rxns (1 x 50 mL) | Order (95138-05K) | |
| PerfeCTa qPCR ToughMix UNG ROX | 1250 x 20 μL rxns (10 x 1.25 mL) | Order (95139-012) |
| 5000 x 20 μL rxns (1 x 50 mL) | Order (95139-05K) | |
| PerfeCTa qPCR ToughMix UNG Low ROX | 1250 x 20 μL rxns (10 x 1.25 mL) | Order (95140-012) |
| 5000 x 20 μL rxns (1 x 50 mL) | Order (95140-05K) |
Documents
Description
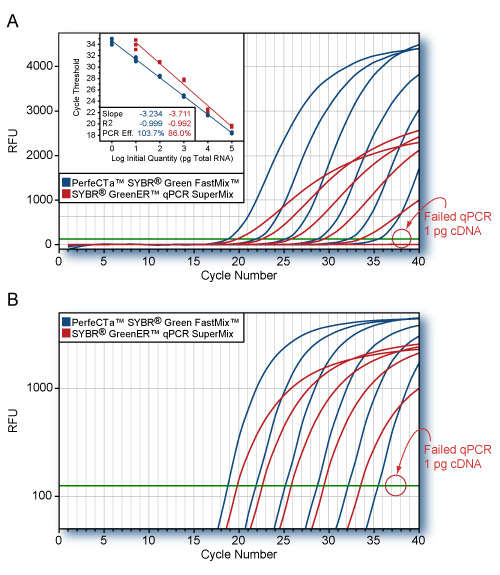
Tough-tested real-time PCR
Features & Benefits
- ToughMix additives neutralize PCR inhibitors to ensure reliable assay performance with a spectrum of starting materials including: clinical specimens, plants, soil, environmental or complex food matrices
- Superior assay sensitivity and target precision with AccuStart™ II enzyme technology – maximum-yielding, engineered Taq DNA polymerase with stringent, ultrapure antibody hotstart
- Easy-to-use 2X concentrated master mixes with AccuVue™ plate loading dye and optimized passive reference dye for simplified reaction setup
- Supports efficient vortex mixing with proprietary anti-foaming technology
- Consistent and reliable performance with exceptional reagent stability (uninhibited after 20X freeze-thaw or 30 days at 22°C)
PerfeCTa qPCR ToughMix is intended for molecular biology applications. This product is not intended for the diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a disease.
Description
PerfeCTa qPCR ToughMix is a 2X concentrated ready-to-use reaction cocktail for PCR amplification of DNA templates that relieves several types of PCR inhibition commonly encountered with crude extracts, environmental specimens, plant tissues, animal tissues, and complex food matrices. This robust real-time qPCR reagent provides maximum sensitivity and PCR efficiency with a variety of fluorogenic probe chemistries, including TaqMan® hydrolysis probes. The only user-supplied components are primers, probe(s), and DNA template. Pre-blended with inert AccuVue plate loading dye to help minimize pipette errors during setup and provides visual confirmation of thorough mixing. A key component of PerfeCTa qPCR ToughMix is an ultra pure, highly processive thermostable DNA polymerase that is combined with high avidity monoclonal antibodies. This proprietary polymerase mix is highly resistant to PCR inhibitors and provides an extremely stringent automatic hot-start allowing reaction assembly, and temporary storage, at room temperature prior to PCR amplification. PerfeCTa qPCR ToughMix delivers exceptional performance with either fast or conventional PCR cycling protocols. UNG containing versions are blended with Uracil N-glycosylase to eliminate potential post-PCR carryover contamination associated with routine molecular testing.
Store components in a constant temperature freezer at -25°C to -15°C protected from light upon receipt. Repeated freezing and thawing does not affect PCR performance. After thawing, mix thoroughly before using. For lot specific expiry date, refer to package label, Certificate of Analysis or Product Specification Form.
Product Flyers
Product Manuals
Publications
Agatha N.Jassem, Journal of Clinical Microbiology – 2016
Abstract
ABSTRACT
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) associated enteric illness is attributed to O157 and non-O157 serotypes, however, traditional culture-based methods under-detect non-O157 STEC. Labor and consumable costs are major barriers for implementation of CDC recommendation of testing all stools for both O157 and non-O157. We evaluated the feasibility of a pooled nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) as an approach for screening of stool specimens for STEC. For retrospective evaluation, 300 stool specimens were used to create pools of 10. The sensitivity was 83% for the pre-enrichment pooling strategy and 100% for the post-enrichment pooling strategy compared with individual NAAT. The difference in cycle threshold between individual and pooled NAAT results for specimens was significantly lower and more consistent for post-enrichment pooling (mean stx1 = 3.90, stx2 = 4.28) compared with pre-enrichment pooling (excluding undetected specimens, mean stx1 = 9.34, stx2 = 8.96) (P≤0.0013). Consumable cost and labor savings of 48-81% and 6-66%, respectively, were estimated for testing of 90 specimens by the post-enrichment pooled NAAT strategy based on an expected 1-2% positivity rate. A 30-day prospective, head-to-head clinical trial involving 512 specimens confirmed the sensitivity and labor savings associated with the post-enrichment pooled NAAT strategy. The post-enrichment pooled NAAT strategy described here is suitable for efficient, large-scale surveillance of all STEC serotypes. Comprehensive detection of STEC will result in accurate estimates of STEC burden and, consequently, appropriate public health interventions.
N.h. Sissener, Aquaculture Nutrition – 2016
ABSTRACT
Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) were fed five graded levels of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5n-3) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6n-3), from 1.4 to 5.2% of total fatty acids (FA, 5–17 mg kg−1 feed), and grew from ~160 g to ~3000 g, with the period from 1450 g onwards conducted both at 6 °C and at 12 °C. All fish appeared healthy, and there were no diet-related differences in haematological or plasma parameters, as well as intestinal histological or gut microbiota analysis. Fish reared at 6 °C had higher accumulation of storage lipids in the liver compared to fish reared at 12 °C. Liver lipids also increased with decreasing dietary EPA + DHA at 6 °C, while there was no such relationship at 12 °C. Gene expression of SREBP1 and 2, LXR, FAS and CPT1 could not explain the differences in liver lipid accumulation. In liver polar lipids, DHA was found to be reduced when dietary EPA + DHA was <2.7% of FAs, while the level of EPA in the membranes was not affected. In conclusion, reducing dietary EPA + DHA from 5.2 to 1.4% of total FAs had a minor impact on fish health. Temperature was the factor that most affected the liver lipid accumulation, but there was also an interaction with dietary components.
Mitochondrial DNA deletion percentage in sun exposed and non sun exposed skin
Julia M. Powers, Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology – 2016
ABSTRACT
The percentages of mitochondrial genomes carrying the mtDNA3895 and the mtDNA4977 (common) deletion were quantified in sun exposed and non sun exposed skin biopsies, for five cohorts of patients varying either in sun exposure profile, age or skin cancer status. Non-melanoma skin cancer diagnoses are rising in Ireland and worldwide [12] but most risk prediction is based on subjective visual estimations of sun exposure history. A quantitative objective test for pre-neoplastic markers may result in better adherence to sun protective behaviours. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is known to be subject to the loss of a significant proportion of specific sections of genetic code due to exposure to ultraviolet light in sunlight. Although one such deletion has been deemed more sensitive, another, called the mtDNA4977 or common deletion, has proved to be a more useful indicator of possible risk in this study. Quantitative molecular analysis was carried out to determine the percentage of genomes carrying the deletion using non sun exposed and sun exposed skin biopsies in cohorts of patients with high or low sun exposure profiles and two high exposure groups undergoing treatment for NMSC. Results indicate that mtDNA deletions correlate to sun exposure; in groups with high sun exposure habits a significant increase in deletion number in exposed over non sun exposed skin occurred. An increase in deletion percentage was also seen in older cohorts compared to the younger group. The mtDNA3895 deletion was detected in small amounts in exposed skin of many patients, the mtDNA4977 common deletion, although present to some extent in non sun exposed skin, is suggested to be the more reliable and easily detected marker. In all cohorts except the younger group with relatively lower sun exposure, the mtDNA4977 deletion was more frequent in sun exposed skin samples compared to non-sun exposed skin.
Three-color crystal digital PCR
J. Madic, Biomolecular Detection and Quantification – 2016
ABSTRACT
Digital PCR is an exciting new field for molecular analysis, allowing unprecedented precision in the quantification of nucleic acids, as well as the fine discrimination of rare molecular events in complex samples. We here present a novel technology for digital PCR, Crystal Digital PCR™, which relies on the use of a single chip to partition samples into 2D droplet arrays, which are then subjected to thermal cycling and finally read using a three-color fluorescence scanning device. This novel technology thus allows three-color multiplexing, which entails a different approach to data analysis. In the present publication, we present this innovative workflow, which is both fast and user-friendly, and discuss associated data analysis issue, such as fluorescence spillover compensation and data representation. Lastly, we also present proof-of-concept of this three-color detection system, using a quadriplex assay for the detection of EGFR mutations L858R, L861Q and T790M.
David Waite, Letters in Applied Microbiology – 2016
ABSTRACT
Citrus canker is an economically important disease caused by the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri (Xcc). This organism targets a wide range of citrus plants, including sweet orange, grapefruit, lemon and lime. As Xcc is spread by environmental factors such as wind and rain, it is difficult to control its movement once the disease has established. In order to facilitate monitoring of citrus canker we sought to design a novel diagnostic protocol based on fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) for identification of bacterial cells directly from canker pustules without cultivation or DNA extraction. This method was validated for specificity against a range of Xanthomonas species and strains. We show that our assay is extremely rapid (typically requiring between two and three hours), and possesses a similar specificity to existing PCR diagnostic tools. The sensitivity of the assay is comparable to that of an existing PCR-based technique and sufficient for identifying Xcc in symptomatic plant material. The method is easily transferable to diagnosticians without prior experience using FISH. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
CofA (PSF)
PSF-95112-012-Lot#020335
PSF-95112-012-Lot#020375
PSF-95112-05k-Lot#020465
PSF-95112-250-Lot#020076
PSF-95113-012-Lot#019921
PSF-95113-012-Lot#020226
PSF-95113-012-Lot#020864
PSF-95113-012-Lot#021026
PSF-95113-012-Lot#021465
PSF-95113-250-Lot#019941
PSF-95114-012-Lot#020323
PSF-95114-05K-Lot#019370
PSF-95114-05k-Lot#020472
PSF-95114-250-Lot#020325
PSF-95140-05k-Lot#020369
PSF-95112-012-Lot#021877
PSF-95112-012-Lot#022197
PSF-95112-012-Lot#023139
PSF-95112-05K-Lot#022233
PSF-95112-05K-Lot#023140
PSF-95113-012-Lot#022025
PSF-95113-012-Lot#022026
PSF-95113-012-Lot#022425
PSF-95113-250-Lot#021887
PSF-95113-250-Lot#021888
PSF-95113-250-Lot#021889
PSF-95113-250-Lot#021941
PSF-95114-012-Lot#021420
PSF-95114-012-Lot#021673
PSF-95114-012-Lot#022021
PSF-95114-012-Lot#023068
PSF-95114-05K-Lot#022132
PSF-95114-05K-Lot#022418
PSF-95114-05k-Lot#021466
PSF-95114-250-Lot#023067
PSF-95138-012-Lot#022242
PSF-95138-05K-Lot#021696
PSF-95138-250-Lot#022130
PSF-95139-012-Lot#022586
PSF-95139-012-Lot#022746
PSF-95139-250-Lot#021716
PSF-95139-250-Lot#021801
PSF-95139-250-Lot#022495
PSF-95139-250-Lot#023374
PSF-95140-012-Lot#021829
PSF-95140-012-Lot#022417
PSF-95140-012-Lot#023452
PSF-95113-012-Lot#023504
PSF-95138-012-Lot#023556
PSF-95112-250-Lot#023895
PSF-95140-05K-Lot#023776
PSF-95112-250-Lot#023950
PSF-95112-250-Lot#023951
PSF-95112-250-Lot#023952
PSF-95114-250-Lot#024055
PSF-95138-250-Lot#024054
PSF-95139-012-Lot#024031
PSF-95112-05k-Lot#024388
PSF-95138-012-Lot#024350
PSF-95138-012-Lot#024351
PSF-95112-05K-Lot#024389
PSF-95112-05K-Lot#024390
PSF-95114-05K-Lot#024468
PSF-95140-05K-Lot#024402
PSF-95112-05k-Lot#020983
PSF-95113-05K-Lot#024526
PSF-95114-250-Lot#024894
PSF-95140-012-Lot#024523
PSF-95140-05K-Lot#024524
psf-95138-05k-Lot#024903
PSF-95112-05K-Lot#025154
PSF-95112-250-Lot#025153
PSF-95139-05K-Lot#025151
PSF-95113-250-Lot#025254
PSF-95138-250-Lot#025417
PSF-95139-012-Lot#025518
PSF-95139-250-Lot#025421
PSF-95112-012-Lot#025606
PSF-95138-05k-Lot#025789
PSF-95112-012-Lot#025606
PSF-95138-05k-Lot#025789
PSF-95112-012-Lot#026173
PSF-95112-250-Lot#026174
PSF-95112-05K-Lot#026172
PSF-95114-250-Lot#026299
PSF-95140-012-Lot#026304
PSF-95140-05K-Lot#026305
PSF-95139-012-Lot#026535
PSF-95139-012-Lot#026536
PSF-95139-250-Lot#026358
PSF-95112-012-Lot#026605
PSF-95112-250-Lot#026604
PSF-95114-05K-Lot#026803
PSF-95138-012-Lot#026799
PSF-95138-250-Lot#026844
PSF-95139-250-Lot#027167
PSF-95112-05K-Lot#027401
PSF-95114-012-Lot#027376
PSF-95114-250-Lot#027377
PSF-95139-012-Lot#027515
PSF-95112-012-Lot#027640
PSF-95112-250-Lot#027639
PSF-95113-250-Lot#027661
PSF-95138-012-Lot#027711
PSF-95138-05K-Lot#027584
PSF-95140-012-Lot#027585
PSF-95140-05K-Lot#027586
PSF-95113-05K-Lot#027889
PSF-95114-05K-Lot#027662
PSF-95139-012-Lot#027910
PSF-95139-05K-Lot#027890
PSF-95139-250-Lot#027908
PSF-95112-012-Lot#028160
PSF-95113-012-Lot#028161
PSF-95114-012-Lot#028163
PSF-95114-250-Lot#028162
PSF-95112-05K-Lot#028112
PSF-95138-250-Lot#028177
PSF-95139-012-Lot#028178
PSF-95140-012-Lot#028179
PSF-95114-05K-Lot#028113
PSF-95138-05K-Lot#028519
PSF-95112-250-Lot#028758
PSF-95114-250-Lot#029136
PSF-95139-012-Lot#029139
PSF-95112-05K-Lot#029437
PSF-95113-250-Lot#029549
PSF-95114-012-Lot#029346
PSF-95114-05K-Lot#029553
PSF-95139-05K-Lot#029527
PSF-95139-250-Lot#029489
PSF-95140-05K-Lot#029428
PSF-95114-012-Lot#029842
PSF-95113-012-Lot#030092
PSF-95140-05K-Lot#030179
PSF-95112-012-Lot#030519
PSF-95112-250-Lot#030385
PSF-95138-05K-Lot#030439
PSF-95113-250-LOT#66139692
PSF-95138-012-LOT#66139696
PSF-95139-012-LOT#66139698
PSF-95140-012-LOT#66139699
PSF-95112-012-LOT#030545
PSF-95112-05K-LOT#030546
PSF-95113-012-LOT#66139430
PSF-95113-012-LOT#66139498
PSF-95114-012-LOT#66139425
PSF-95114-012-LOT#66139500
PSF-95114-250-LOT#66140235
PSF-95140-250-LOT#66140748
PSF-95138-250-LOT#66141466
PSF-95139-012-LOT#66141467
PSF-95139-05K-LOT#66141468
PSF-95139-250-LOT#66141469
PSF-95112-250-LOT#66141371
PSF-95114-05K-LOT#66141372
PSF-95140-05K-LOT#66141470
PSF-95112-250-LOT#66147415
PSF-95112-012-LOT#66148053
PSF-95114-250-LOT#66147880
PSF-95112-05K-LOT#66148044
PSF-95138-05K-LOT#66141465
PSF-95138-250-LOT#66148818
PSF-95140-250-LOT# 66147974
PSF-95112-05K-LOT#66149651
PSF-95112-250-LOT#66149653
PSF-95114-05K-LOT#66149654
PSF-95138-05K-LOT#66150133
PSF-95139-250-LOT#66149656
PSF-95139-05K-LOT#66151933
PSF-95112-05K-LOT#66152716
PSF-95114-012-LOT#66148646
PSF-95113-012-LOT#66153246
PSF-95113-05K-LOT#66153431
PSF-95113-250-LOT#66153245
PSF-95114-05K-LOT#66154302
PSF-95138-012-LOT#66154171
PSF-95138-05K-LOT#66154169
PSF-95138-250-LOT#66154380
PSF-95114-05K-LOT#66155748
PSF-95112-05K-LOT#66155887